MEE Subjects
The Multistate Essay Examination (MEE) tests a wide range of topics, assessing your ability to apply legal principles, analyze complex issues, and craft clear, concise responses.
Each administration includes 6 essay questions drawn from the following 12 subjects:
- Business Associations
- Civil Procedure
- Conflict of Laws
- Constitutional Law
- Contracts and Sales
- Criminal Law and Procedure
- Evidence
- Family Law
- Real Property
- Torts
- Trusts and Estates
- Secured Transactions (UCC Article 9)

Business Associations
Business Associations explores the legal foundations of corporations and partnerships, covering their creation, management, and dissolution.
Key topics include:
- Duties and responsibilities of directors and officers
- Shareholder rights and governance
- Legal complexities in business sales
- Fiduciary obligations within corporations
- Liability issues in partnership structures
This MEE subject is tested under 2 areas: Agency and Partnerships and Corporations and LLCs. These topics may be assessed individually or integrated into a single question.
Civil Procedure
Civil Procedure has appeared on the MEE every year since 2014 and is the most frequently tested subject. It covers the rules and procedures that courts must follow in civil cases, including how lawsuits are initiated, the steps involved in litigation, and the principles governing the jurisdiction and authority of courts.
Key topics include:
- Personal jurisdictions
- Subject matter jurisdiction
- Venue selection
- Different stages of a lawsuit: pleadings, discovery, trial procedures, and post-trial motions
- Federal-state relations and conflicts involving the Full Faith Credit Clause and the Erie Doctrine

Conflict of Laws
Conflict of Laws, also known as Private International Law, involves cases where the laws of different jurisdictions intersect, including determining which jurisdiction’s laws apply to a case involving cross-border elements. The subject typically appears alongside family law, torts, and contracts, especially where these issues cross state or national boundaries.
Key topics include:
- Domicile
- Choice of law
- Jurisdiction
- Choice of law
- The recognition and enforcement of judgments from other jurisdictions
Constitutional Law
Constitutional Law focuses on interpreting and applying the U.S. Constitution, addressing the structure of the federal government, the powers and limits of its branches, and the rights guaranteed to individuals.
Key topics include:
- Judicial review
- Federalism
- Application to modern issues
- Protection of rights.
- Conflicts between rights and government interests
Contracts and Sales
Contracts and Sales examines the principles governing the creation, interpretation, and enforcement of agreements between parties, as well as remedies for breaches.
Key topics include:
- Formation of contracts
- Breach of contract
- Defenses to enforcement
In addition to these foundational elements, UCC Article 2 governs the sale of goods, addressing unique aspects like warranties, risk of loss, and the statute of frauds. A strong understanding of common law principles and UCC provisions will help you master this subject.
Criminal Law and Procedure
Criminal Law and Procedure encompasses the legal principles and rules designed to keep the public safe and deter wrongful conduct. About half of the questions in this section will focus on the constitutional rights of those accused of a crime. The other half covers the definitions of criminal offenses, the rights of the accused, and the procedural steps from investigation to trial, sentencing, and appeals.
Key topics include:
- Homicide
- Other crimes (e.g., theft, assault)
- Inchoate offenses (attempts, conspiracy, solicitation)
- Defenses to crimes
- Constitutional protections for accused persons
- The process of criminal adjudication
Criminal Law and Procedure is a staple of the MEE, reflecting its fundamental role in the U.S. legal system. It is tested with moderate frequency, often focusing on the elements of major crimes, defenses, and constitutional safeguards during criminal proceedings.
Evidence
Evidence law governs the introduction of evidence presented at civil and criminal trials, specifying what information is admissible to judge the merits of a case. Ensure you answer these questions per the Federal Rules of Evidence, not your jurisdiction's rules of evidence. The presentation of evidence (objections, impeachments, etc.), hearsay, and relevancy make up over 80% of this issue.
Key topics include:
- Relevance
- Hearsay and its exceptions
- Character evidence
- Privileges
- The best evidence rule
- Impeachment of witnesses
Evidence is a highly tested area on the MEE, emphasizing its critical role in legal proceedings. Exam questions often revolve around the admissibility of evidence and its impact on trial outcomes.

Family Law
Family Law addresses legal issues related to domestic relations and family matters. In most situations, family law is tested independently. However, a Conflict of Laws problem does arise on occasion.
Key topics include:
- Marriage and divorce
- Child custody and support
- Adoption and paternity
- Marital property rights
- Domestic violence protection
Family Law questions on the MEE often emphasize these recurring topics, requiring you to apply foundational principles to practical scenarios, such as contested custody disputes and asset division.
Real Property
Real Property addresses the legal framework governing land, improvements, and related rights, often tested on the MEE through scenarios involving ownership, land use, and real estate transactions.
Key topics include:
- Ownership rights and interests
- Land use and zoning
- Easements and covenants
- Landlord-tenant issues
- Sales and financing of real property
Proficiency in these topics is crucial for addressing common property law issues, such as resolving title disputes, enforcing land use agreements, and managing landlord-tenant conflicts in real-world and exam settings.
Torts
People who have been wronged in some way, whether physically or financially, can often find recourse under tort law. Intentional torts, strict responsibility, product liability, and other torts will make up the other half of the questions in this section (nuisance, defamation, invasion of privacy, etc).
In this field of law, the National Conference of Bar Examiners (NCBE) advises you to assume:
- Survival actions and wrongful death claims are available where appropriate.
- Standards for pure comparative blame and joint and several liability apply unless otherwise stated.
Tort law involves civil wrongs causing harm or injury, where the injured party may seek compensation. It covers:
- Negligence
- Intentional torts
- Strict liability
- Defamation
- Privacy torts
Trusts and Estates
Trusts and Estates encompass the legal frameworks for managing and distributing property during life and after death. It is tested independently on the MEE, typically appearing once or twice every 2 years. This subject requires a strong understanding of foundational and nuanced principles.
Key topics include:
- Decedents’ estates
- Wills
- Family protection mechanisms
- Living wills and durable healthcare powers
- Trusts and future interests
This area of law is integral to estate planning, ensuring orderly property distribution and resolving disputes involving fiduciary duties, contested wills, and trust administration. Proficiency in these concepts is crucial for addressing real-world challenges and excelling in MEE scenarios.
Secured Transactions
Secured Transactions focuses on the rules established under Article 9 of the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC), which governs security interests in personal property. This subject is critical for the MEE, particularly for its application in commercial and financial contexts. Article 9 provides the framework for creating, prioritizing, and enforcing security interests in movable property, fixtures, and certain intangibles.
Key concepts include:
- Attachment and perfection
- Priority rules
- Foreclosure and repossession
- Effects of default
Success on Secured Transactions questions often requires precise application of these principles to analyze conflicts between creditors, assess the validity of secured interests, and resolve disputes involving debtor defaults.
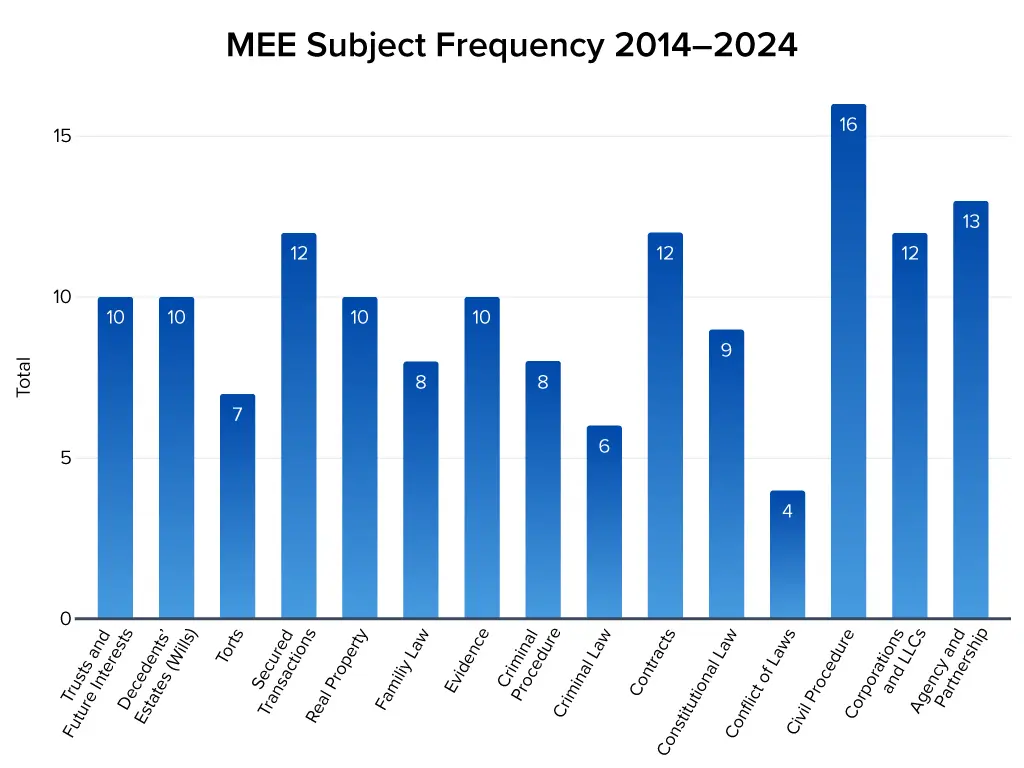
MEE Subject Frequency and Pairing Patterns
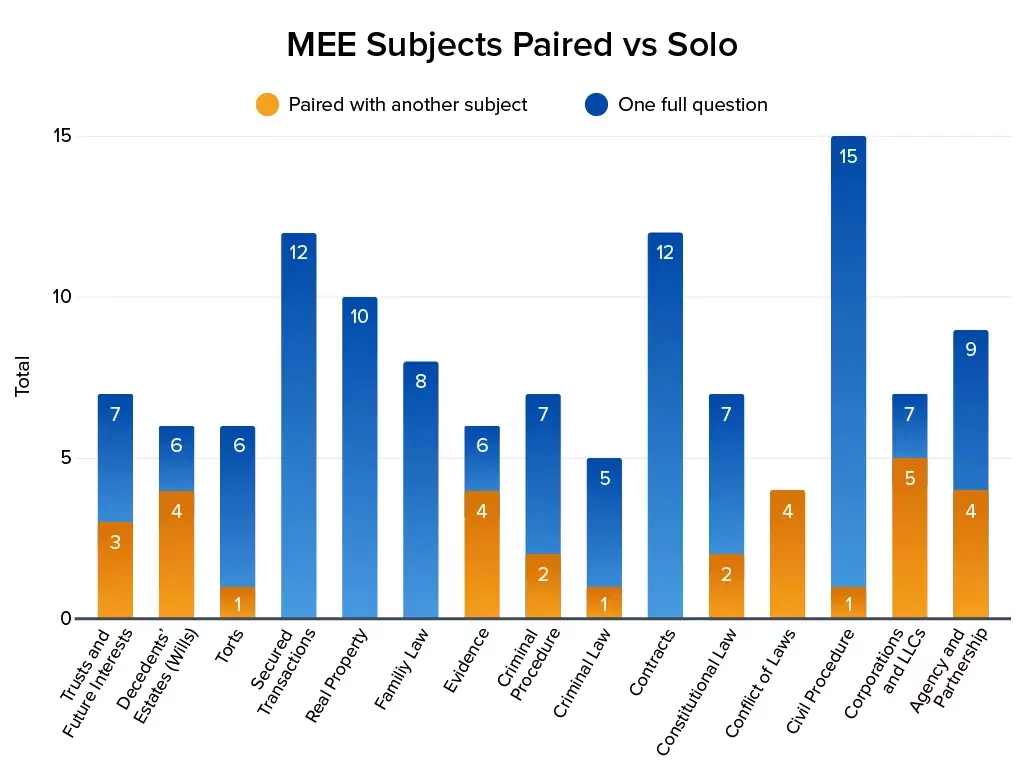
Subjects such as Civil Procedure appear on almost every exam and should be prioritized during preparation. Others, such as Conflict of Laws and Criminal Law, appear less frequently but are often paired with other topics. For example, Conflict of Laws may accompany Family Law or Contracts, while Real Property is usually tested alone. Understanding these patterns allows you to allocate study time efficiently, focusing on high-yield subjects while covering less common areas strategically.
Sometimes, the NCBE tests MEE subjects together in a single question. Anything is fair game. For example, Conflict of Laws is always tested with another subject, while Real Property is generally tested as a single question. See the chart below for how often subjects are tested alone or paired with another.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good score on the MEE?
How should I allocate my study time for the MEE?
Effective preparation starts with prioritizing high-frequency subjects such as Civil Procedure and Business Associations while dedicating time to less-tested but critical areas. Balance your study schedule to focus on mastering foundational topics and improving weak areas through consistent practice.
Which subjects are tested more frequently on the MEE?
The most frequently tested subjects on the MEE are Business Associations, Trusts and Estates, Civil Procedure, and Conflict of Laws.
How does the NextGen Bar Exam influence MEE preparation?
The NextGen Bar Exam emphasizes practical application and integrated assessments, requiring a stronger focus on problem-solving and real-world legal scenarios.
What strategies can improve my performance on paired questions?
Paired questions often test the intersection of multiple subjects, such as Conflict of Laws with Family Law. To excel, ensure you understand the individual subjects thoroughly and practice identifying how their principles interact in complex scenarios. Reviewing NCBE analyses of past paired questions can provide insight into examiner expectations.
What role does structure play in MEE scoring?
Structure is vital in MEE essays, as graders work under time constraints. Clear headings, logical flow, and concise writing make your answers easier to follow, ensuring you earn points for substance and presentation. Practice organizing your responses to address all issues methodically and effectively.