The bar exam’s format and tested subjects vary across jurisdictions, with most states using the Uniform Bar Exam (UBE®) and others incorporating state-specific subjects or using 1 or more UBE components. Beginning in July 2026, the NextGen Bar Exam will replace the legacy UBE in select jurisdictions before rolling out more broadly through 2027 and 2028.
This guide breaks down the current legacy UBE format and subjects, how non-UBE states structure their exams, and what to expect from the NextGen UBE as it begins its transition period in 2026-27.
The UBE is administered over 2 days and tests legal knowledge and practical skills through 3 components:
- Multistate Bar Examination (MBE®)
- Multistate Essay Examination (MEE®)
- Multistate Performance Test (MPT®)
Day 1 includes 2 MPT tasks in the morning and 6 essay questions in the afternoon, while day 2 is devoted to the MBE, with 100 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) in the morning and afternoon sessions.
| UBE Structure | ||
|---|---|---|
| Session | Tuesday | Wednesday |
|
Morning (3-hour session) |
2 MPTs | 100 MBE MCQs |
|
Afternoon (3-hour session) |
6 essay questions | 100 MBE MCQs |
MEE
The MEE includes 6 essay questions in 3 hours. Each presents a hypothetical scenario that may test a single subject or a mix of topics. Not all subjects appear on every exam, so you must be prepared to identify key issues quickly and apply the relevant legal rules clearly and efficiently.
Learn More
MPT
The MPT consists of 2 90-minute tasks that simulate real legal work, such as drafting a memo or letter. All necessary materials, such as case files and rules, are provided in the fictional jurisdiction of “Franklin”, and no outside knowledge is required. The exam tests your ability to apply facts to law, solve problems, and communicate effectively in writing.
Learn More
MBE
The MBE is a 200-question multiple-choice exam split into 2 3-hour sessions. It uses hypothetical scenarios to test how you apply legal principles across multiple topics. Each question has 4 answer choices with challenging distractors, and the exam emphasizes analytical reasoning over memorization.
Learn More
Subjects and Topics
The UBE tests a broad range of subjects to assess a candidate’s grasp of fundamental legal principles and practical lawyering skills. The exam covers 12 subjects divided between the MBE and the MEE. Some subjects are tested in both sections, while others are only tested on the MEE. Below is a breakdown of the core subjects and key topics that may appear on the UBE.
| Subject | Key Subtopics | Brief Summary | Exam Section |
|---|---|---|---|
| Civil Procedure | Jurisdiction, pleadings, motions, pretrial procedure, trial procedure, judgments, appeals | Covers the rules governing civil litigation in federal courts | MBE, MEE |
| Constitutional Law | Federalism, separation of powers, individual rights, First Amendment | Focuses on the powers of the government and the rights of individuals under the Constitution | MBE, MEE |
| Contracts | Contract formation, defenses, breach, remedies, third-party rights | Governs the formation and enforcement of contracts, as well as remedies for breach | MBE, MEE |
| Criminal Law and Procedure | Crimes, inchoate offenses, defenses, and constitutional protections for the accused | Covers substantive criminal law and the procedural protections of the accused | MBE, MEE |
| Evidence | Relevance, hearsay, privileges, burdens of proof, and admissibility | Deals with the admissibility of evidence in trials and legal proceedings | MBE, MEE |
| Real Property | Ownership, rights in land, landlord-tenant law, mortgages, property transfers | Covers issues related to property ownership, transfers, and land use | MBE, MEE |
| Torts | Negligence, intentional torts, strict liability, product liability, defenses | Governs liability for harm caused by 1 party to another, whether intentional or through negligence | MBE, MEE |
| Business Associations | Corporations, partnerships, LLCs, fiduciary duties, agency | Addresses the structure and governance of business entities, including corporations and partnerships | MEE |
| Conflict of Laws | Choice of law, recognition of judgments, and jurisdictional issues | Addresses issues arising from differences in laws between jurisdictions | MEE |
| Family Law | Marriage, divorce, child custody, adoption, support | Covers the legal aspects of marriage, divorce, and parental rights | MEE |
| Trusts and Estates | Wills, intestacy, trusts, and fiduciary duties of trustees | Covers the transfer of property upon death and the administration of trusts | MEE |
| Secured Transactions | Creation, perfection, priority of security interests under Article 9 UCC | Covers secured transactions in personal property, focusing on creditor rights | MEE |
Component Weight and Distribution
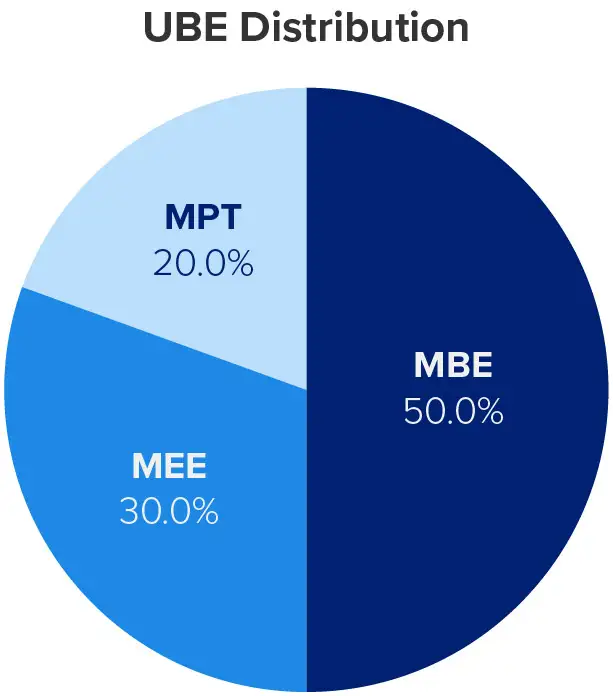
The UBE’s weight distribution — 50% MBE, 30% MEE, and 20% MPT — balances legal knowledge with practical skills. Since the MBE makes up half of your score, strong performance here can offset weaker results on the MEE or MPT.
Conversely, a low MBE score requires higher MEE and MPT scores to compensate. The MBE is also scaled, meaning scores are adjusted based on how others perform, adding some variability.
Learn More
The UBE is administered over 2 days and tests legal knowledge and practical skills through 3 components:
The NextGen UBE tests legal knowledge and practical skills. It comprises 3 sections of 3 hours each, administered over 1.5 days (9 hours), replacing the legacy UBE sections. Each exam section contains a combination of:
- 40 standalone MCQs: 72 minutes
- 2 integrated question sets: 48 minutes
- 1 performance task: 60 minutes
You have 1.8 minutes per MCQ, 24 minutes per integrated question set, and 60 minutes per performance task.
| NextGen UBE Structure | ||
|---|---|---|
| Session | Tuesday | Wednesday |
|
Morning (3-hour session) |
Section 1 | Section 3 |
|
Afternoon (3-hour session) |
Section 2 | N/A |
Standalone Multiple-Choice Questions
Standalone multiple-choice questions come in 2 formats: select 1 answer from 4 choices or 2 from 6. Each section has 40 questions, for a total of 120 on the exam. They cover 8 Foundational Concepts and Principles; some questions may touch on more than one area.
Integrated Question Sets
Integrated question sets are grouped around a shared fact scenario and come in 2 formats: drafting sets with medium‐answer questions and counseling sets with short‐answer and multiple‐choice questions. Each section includes 2 sets, for a total of 6 on the exam. They test how well you apply Foundational Skills in realistic situations and may introduce legal topics outside the Foundational Concepts, with resources provided when needed.
Performance Tasks
Performance tasks also appear in 2 formats: standard tasks with a single longer writing assignment, and legal research tasks with multiple-choice and short-answer questions followed by a medium-length written response. Each exam section includes 1 task, for a total of 3. They test how well you apply Foundational Skills in realistic lawyering situations, with a case file and library provided for reference.
NextGen Subjects and Topics
The NextGen UBE tests range of skills and concepts to assess a candidate’s readiness. The exam covers 8 foundational concepts and principles, instead of 12 in legacy UBE, divided across 3 sections. Below is a list of skills tested from July 2026 to February 2028:
| Foundational Concepts and Principles | Foundational Skills Tested |
|---|---|
| Business Associations and Relationships | Legal research |
| Civil Procedure | Legal writing |
| Constitutional Law | Issue spotting and analysis |
| Contract Law | Investigation and evaluation |
| Criminal Law and Constitutional Protections of Accused Persons | Client counseling and advising |
| Evidence | Negotiation and dispute resolution |
| Real Property | Client relationship and management |
| Torts |
NextGen Component Weight and Distribution
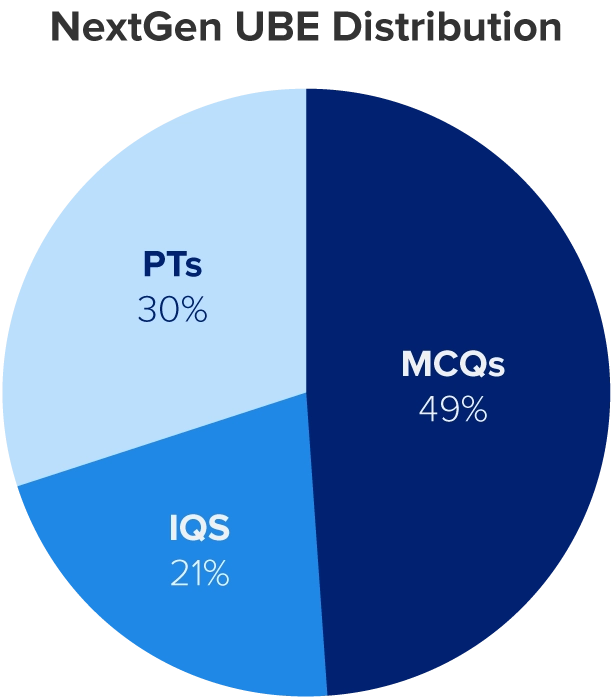
The NextGen’s UBE’s weight distribution — 49% standalone MCQs, 21% integrated question sets, and 30% performance tasks — balances legal knowledge with practical skills.
The official NextGen UBE scores will be reported as a single number scaled from 500 to 700, with each jurisdiction setting its passing score within the range.
Partial scoring is available for all the exam question types and sections.
Non-UBE States Bar Exam Format, Subjects, and Topics
While most jurisdictions have adopted the UBE and will subsequently implement NextGen UBE, some states continue to administer their unique bar exams. These non-UBE states often include state-specific components alongside UBE components. For example:
- California tests state-specific subjects, such as Community Property and the MBE.
- Louisiana focuses on Civil Law rather than Common Law, reflecting its French and Spanish legal traditions.
- Due to the state’s prominence in corporate litigation, Delaware emphasizes Business and Corporate Law.
Select a non-UBE state below for more information:
| Non-UBE States | ||
|---|---|---|
| California | Delaware | Florida |
| Guam | Georgia | Hawaii |
| Louisiana | Mississippi | Nevada |
| Northern Mariana Islands | Palau | Puerto Rico |
| South Dakota | Virginia | Wisconsin |